Learn how we helped a midstream company create and implement a PSM-compliant reliability program for its greenfield fractionation facility.
Challenge
A midstream company needed to establish a reliability program for a new fractionation facility to comply with OSHA’s PSM standards.
Solution
Pinnacle strategically partnered with the company to design, build, and implement a PSM-compliant reliability program prior to startup.
Result
The facility was PSM-compliant from startup and currently operates at a 109% nameplate capacity.
The Challenge
A midstream company that primarily focuses on pipeline construction and operation built a new fractionation facility that fractionates Y-grade natural gas liquids into propane, butane, isobutane, and natural gasoline. The fractionation facility is the company’s first asset that falls under Occupational Safety and Health Administration’s (OSHA) Process Safety Management (PSM) standards. Because the company primarily focuses on pipeline construction and operation, they needed help ensuring their processes and reliability program are compliant with PSM standards.
The company did not have a standard reliability program in place prior to construction of the facility. Additionally, the company did not have a Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) or Inspection Data Management System (IDMS) in place, making it difficult for its team to track, manage, and analyze data. Any data the facility had was inconsistent and was stored in siloed systems. Without proper data systems in place, the company was unable to track and report the data needed to be compliant with PSM standards.
The company had an overall goal to operate safely and reliably but had difficulty defining how it could tangibly incorporate this goal into its reliability program. Pinnacle was brought in to develop a reliability strategy that would ensure its program was designed with reliability in mind from the start.
Pinnacle's Solution
Despite being a challenge, creating a new reliability program from scratch was a great opportunity for the company to build its program based on strong reliability fundamentals. The Pinnacle team worked with the company to take its vision and turn it into a robust, well-documented reliability program. The project consisted of three phases:
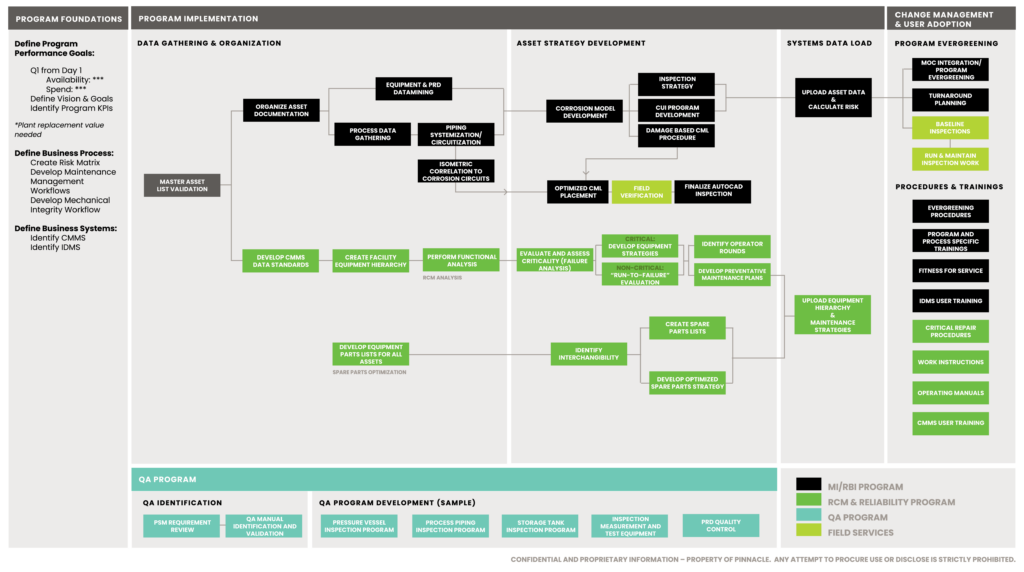
Phase 0: Program Foundations Development
In Phase 0, Pinnacle worked with the facility to develop its reliability program and establish a strong foundation for Phase 1 and 2. In this phase, the Pinnacle team built and reviewed all program requirements that the facility needed to be PSM-compliant prior to startup. Additionally, the Pinnacle team developed a risk matrix and the standards and workflows for maintenance and mechanical integrity (MI).
Risk Matrix Development:
Pinnacle facilitated a one-day workshop with site personnel to create a risk matrix to manage RBI results for current and future site implementations. This risk matrix was implemented into the site’s IDMS during a later phase and applied to other criticality analyses and RBI studies across the facility, resulting in a consistent way to drive business decisions across implementations moving forward.
Maintenance Standard and Workflow Development:
The team developed a list of standards and workflows that defined the necessary processes for the facility to have a proactive, damage-based program. These standards included maintenance management, materials management, and CMMS data standards. Additionally, repair procedures and a spare parts list and strategy for critical assets were included to reduce downtime when unexpected maintenance is needed.
Mechanical Integrity Standard and Workflow Development:
The team created a list of standards and workflows for implementing and maintaining the site’s MI program. These standards include elements such as the list of necessary program procedures, RBI-generated inspection recommendations, and damage mechanism application and mapping within an IDMS.
Additionally, Pinnacle provided a list of PSM requirements that were later implemented during Phase 1.
Phase 1: Holistic Program Implementation
Pinnacle implemented RBI and RCM programs at the fractionator facility to minimize future failures, costs, and associated downtime. During this phase, all of the facility’s asset data was gathered, analyzed, and loaded into the facility’s IDMS. Additionally, baseline condition monitoring locations and visual inspections for the facility’s piping and equipment were completed. Equipment hierarchy, maintenance strategies, and spare parts strategies were developed for all the facility’s assets. Because the Pinnacle team had helped set up the IDMS, it was a simple addition to upload the facility’s field data after conducting the inspections.
Mechanical Integrity
Data Gathering and Organization:
The facility’s Master Asset List (MAL) was cross-referenced with the facility’s piping and instrumentation diagrams (P&IDs), process flow diagrams (PFDs), design packages, and personnel interviews. An electronic documentation library (EDL) was developed, all units were systemized, and the facility’s P&IDs were circuitized based on similar operating conditions and expected damage mechanisms. Additionally, the Pinnacle team took baseline readings, placed condition monitoring locations (CMLs), and conducted external inspections for all piping and equipment. Pinnacle conducted these external inspections from a QA/QC standpoint to ensure all piping was insulated correctly and there was no existing damage to the coating.
Asset Strategy Development:
This strategy consisted of developing corrosion models that assessed each circuit to model a predictive corrosion rate for each anticipated damage mechanism, a damage mechanism review, the identification of consequence of failure, isometric drawing correlation, corrosion control documents (CCDs), integrity operating windows (IOWs), and CML placement.
IDMS Data Load and Configuration:
The Pinnacle team worked with the facility to select an IDMS system that worked best for the facility’s processes and helped set up the system, configures inspection events and schedules, and establish data hierarchy. Among the many benefits that the facility recognized from this step, among the most important were the uploading and organization of piping and pressure relief device (PRD) data, risk calculations and validations, and baseline inspection preventive maintenance schedule creation.
Field Services:
The Pinnacle team performed baseline inspections including external and internal API 510 and 570 inspections. Additionally, the team performed baseline thickness inspections and resulting data into the IDMS.
Reliability
Pinnacle implemented a Reliability Centered Maintenance (RCM) program, which included the selection and configuration of a CMMS and the development of a comprehensive asset hierarchy. This step also included a full risk assessment of the facility’s assets which was used to create proactive maintenance strategies, job plans, and spare parts list to reduce downtime when unexpected maintenance is needed. Pinnacle achieved this through:
Asset Hierarchy:
The Pinnacle team worked with the facility to develop a comprehensive asset hierarchy.
RCM:
An RCM analysis of the facility was completed. This analysis also included a Failure Modes, Effects, and Criticality Analysis (FMECA), risk assessment, and a proactive maintenance program for in-scope equipment.
Proactive Maintenance and Operator Rounds:
The team developed new maintenance job plans, proactive maintenance schedules, and operator rounds. These documents were implemented into the facility’s CMMS.
Spare Parts:
A spare parts analysis for all equipment including machinery skids, electrical equipment, and valves, was conducted to determine spare parts recommendations.
Detailed Repair Procedures:
The Pinnacle team worked with facility personnel to develop detailed repair procedures for the most common failure modes on selected equipment.
Predictive Monitoring and Condition-Based Analysis
Phase 2: Continuous Improvement and Long-Term Support
The third phase consists of the evergreening and long-term support of the facility. This phase helps the facility continually improve and sustain low costs while achieving high availability. This support is primarily done through inspection, RBI evergreening, and continued PSM compliance support.
Results
Pinnacle serves as the company’s sole partner in managing all of its reliability needs. As a result of the holistic program implementation, the facility has the documentation, procedures, and tools needed to meet PSM compliance and is able to operate at 109% nameplate capacity.
As an example of the program’s success, a failing pump bearing was identified through vibration analysis and was replaced at the next scheduled maintenance interval. Because the facility was able to proactively identify and schedule the repair, the bearing replacement did not interfere with the facility’s operations.
Pinnacle continues to evergreen the facility’s IDMS, CMMS, and vibration and lube oil analysis. Additionally, Pinnacle has an onsite presence that helps with day-to-day issues such as interpreting API standards to locate critical spare parts.
Conclusion
By monitoring asset health through risk-based programs, consolidating all asset data into organized databases through data-driven reliability, and trending asset degradation and maintenance based on captured findings, this facility has set itself up for success in maintaining safe and reliable operations.
Stay in the know.
Providing data-driven insights, perspectives, and industrial inspiration from the forefront of the reliability transformation.