Learn how we helped a wastewater treatment facility reduce their total cost of ownership and improve maintainability.
Challenge
A wastewater treatment facility is currently undergoing an estimated $1.7B capital expansion to increase water treatment capabilities due stricter regulations. The facility needed a long-term, cost-effective way to maintain critical assets and ensure the lowest total cost of ownership.
Solution
Pinnacle supported the facility’s objectives by introducing Reliability Centered Design (RCD) and Reliability Centered Maintenance (RCM) principles in the front-end engineering design phase through commissioning.
Result
The facility is now able to start-up with a complete reliability and maintenance program in place from day one, ensuring compliance and the safety of its workforce and an estimated $100MM in cost savings over the life of the facility.
The Challenge
The Sacramento Regional Wastewater Treatment Plant (Regional San) serves a population of approximately 1.6 million and discharges treated effluent into the Sacramento River. In 2010, the facility received new, stricter treatment and discharge requirements from the state of California requiring the removal of ammonia and nitrate residuals from the treated water prior to discharge.
In response to the new requirements, Regional San began a major capital upgrade, which they named the “EchoWater Project.” This project involved upgrading the plant to include more advanced treatment capabilities and required the facility to design and build new treatment infrastructure which is currently in process and is scheduled for completion in 2023.
Regional San reports the EchoWater project will provide “…the most significant upgrade to [the] wastewater treatment plant since its original construction…[and] will produce cleaner water for discharge to the Sacramento River [or] for potential reuse as recycled water.”
To manage the costs of this expansion while driving reliability and maintainability, the facility needed to implement strategies that would improve design, optimize capital and operational expenditures, and streamline operations and maintenance (O&M). For these reasons, the facility leaders decided to implement Reliability Centered Design (RCD) and Reliability Centered Maintenance (RCM) as a means to reduce total cost of ownership. With their end goal in mind, facility leaders sought out a third party to assist with implementing these reliability and maintainability strategies.
Pinnacle's Solution
Pinnacle was brought into the project during the front-end engineering design stage to facilitate an RCD analysis. Once the design was completed, Pinnacle supported the implementation of an RCM program to ensure personnel had a streamlined, safe, and cost-effective program in place prior to assuming ownership of the facilities.
The typical process includes:
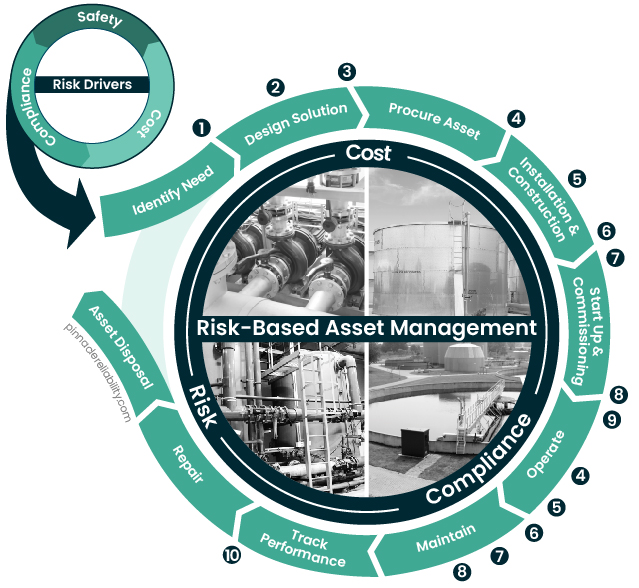
1. Reliability Availability Maintainability Modeling (RAM Modeling)
RAM Modeling is used to simulate probable future performance metrics of the process design. The output of RAM Modeling quantifies the performance criteria of equipment-related decisions such as redundancy, spare parts, and equipment sizing. RAM Modeling assesses the longevity and long-term reliability of the system and its components.
2. Reliability Centered Design (RCD)
3. Specification Development Assistance
4. Reliability Centered Maintenance (RCM)
5. Task Selections
6. Develop O&M Documents
7. Computer Maintenance Management System (CMMS) Upload
8. Reliability Training
9. Management of Change (MOC)
10. Reliability Evergreening
Results
By implementing reliability-centered principles and focusing on the total asset lifecycle, Regional San now has an optimized way to maintain the facility’s equipment and a means of categorizing equipment in order to prioritize corrective maintenance activities under various conditions. This is especially important during seasonal peak wet weather inflows. Additionally, a streamlined RCM approach that leveraged Reliabuilder©, Pinnacle’s proprietary software, projected that the facility would start to see a return on investment in only nine months. Additionally, this analysis projected that Regional San would recognize an estimated $100MM in cost savings over the life of the facility, about 50 years.
Additional benefits included:
Design Improvements and Optimized Costs
- Pinnacle worked with Regional San’s EchoWater Program Management Office to identify hundreds of reliability-based, one-time opportunities for design improvements. A majority of these improvements were accepted into the finalized designs. The recommendations implemented during the facility’s expansion relate to engineering, process, or safety improvements, as well environment and regulatory considerations which are meant to prevent costly shutdowns or redesign issues. They also cover initial spare parts stocking recommendations for assets that are critical to process or safety, and for spare parts with long lead times that are not readily available.
- From the data gathered through RCM process interviews and task selection workshops held together with Regional San’s site personnel, Pinnacle performed analysis on process operability, which defines consequential criticality and abbreviated operator response corrective actions required to address any potential process functional failures. This focus on maintaining system-wide availability based in an operational context was used to first identify conditions which could have shut down half of one of the main treatment systems, and from there, home in on key maintenance strategies to prevent regulatory fines that could have resulted from this scenario. Maximizing process uptime and availability of all assets even during abnormal situations is a key feature both the RCD and RCM processes.
- Streamlined warranty PM from vendors. Instead of using default vendor recommendations, Pinnacle proposed a streamlined approach which only implemented the most beneficial warranty PMs on critical assets which were evaluated to have a repair or replacement value of $25K or greater. The total operating maintenance cost will be reduced through the implementation of reliability-centered maintenance principles and a focus on condition-based tasks.
- Working with Regional San’s O&M group, Pinnacle leveraged its vast industry experience to help optimize future spare parts inventory requirements to ensure critical parts will be available when needed while maintaining availability and performance and reducing cost to own and operate. In general, spare parts optimization typically results in cost reduction of around 20% to 50%, and in some cases, as high as 75% as compared to buy and stock methods. Updated storage practices were recommended to keep the necessary spare parts from deteriorating due to exposure to Ultra-Violet (UV) radiation, electrostatic discharge, corrosive vapors, contamination, or moisture intrusion.
Increased Reliability and Safety
- Job plans, preventative maintenance schedules, Lockout Tagout procedures (LTVs), and other operating documents were provided to Regional San to be uploaded into their CMMS prior to startup so that the facility would be ready to start tracking performance of assets and labor.
- Operator rounds—in which operators take on basic maintenance tasks—were developed. Operators assisting with maintenance tasks can help minimize repair costs, reduce downtime, mitigate or eliminate safety hazards, and extend equipment life.
- LOTO program development. Per OSHA 1910.146, LOTO is required for both proactive and corrective maintenance to be in a zero-energy state. The facility’s existing practice was to develop LOTOs as needed, and Pinnacle developed a program in which the LOTOs were predeveloped/preapproved for each repair task and linked to the job plans. This reduces mean time to repair and subsequent labor costs at the same time, while upholding a world-class safety culture.
Upon completion, the EchoWater project at Regional San is estimated to cost about $1.7 billion USD in capital expenditures and approximately $50 million USD in increased yearly operations and maintenance costs per year.
By implementing RCD and RCM, the EchoWater expansion now has a risk-based reliability strategy built into its design and daily operations and maintenance programs. This optimized, data-driven reliability program is focused on protecting rate payers from future utility rate increases and sustaining system performance and compliance at the lowest cost without impacting asset lifecycle costs. As the project nears completion, the results of optimizing the labor, energy, operations and safety requirements give Regional San and the surrounding customers the security of knowing they have state of the art, critical infrastructure protecting their health as well as the environmental stewardship of one of California’s most important resources at the pinnacle of efficiency.
Stay in the know.
Providing data-driven insights, perspectives, and industrial inspiration from the forefront of the reliability transformation.